
Research has shown that maintaining out-of-home mobility is of great importance for people moving to old age from late midlife. The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.Ĭompeting interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.įitness to drive in the geriatric population and the potential effects of cognitive and physical decline remain a difficult challenge for primary care physicians. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.ĭata Availability: All data and statistical analysis files are available in Zenodo ( ).įunding: BF and PV were supported by a grant from the Department of Medicine and Community Health of the University Hospital of Lausanne, Switzerland. Received: Accepted: AugPublished: August 20, 2021Ĭopyright: © 2021 Kokkinakis et al. Akinwuntan, University of Kansas Medical Center, UNITED STATES The availability of such valid and practical assessment suggests the feasibility of integrating the technology within a clinical algorithm for improved detection of cognitive decline.Citation: Kokkinakis I, Vaucher P, Cardoso I, Favrat B (2021) Assessment of cognitive screening tests as predictors of driving cessation: A prospective cohort study of a median 4-year follow-up. 001).Mindstreams was easily employed, including in patients with considerable cognitive impairment, supporting its practicality for in-office cognitive assessment of the elderly. Seventy-eight percent of ratings for non–computer users, 76% for patients older than 75, and 74% for poor performers indicated no frustration (Ps <. For all patients, 76% of supervisor ratings indicated no patient frustration (P <. Supervisor ratings and ease of understandability ratings were similar. Seventy-three percent of non–computer users, 70% of patients older than 75, and 69% of poor performers rated them easy to use (Ps <. Separate analyses were run for non–computer users, patients older than 75 years, and poor performers (≤1 standard deviation on overall battery performance).For all patients (n = 2,888 age, 64.7 ± 18.2 years), 83% rated the tests easy to use (P <. The χ2 goodness-of-fit test was employed to determine whether patients and supervisors more often rated tests easy versus hard to use. This study evaluated its feasibility for assessment of the elderly.Usability data were collected after each of 2,888 consecutive initial-visit testing sessions at the first 11 clinical centers to use Mindstreams. Mindstreams is an office-based computerized system for measuring cognitive function in multiple domains, with demonstrated validity, test-retest reliability, and sensitivity to treatment effects. However, many early cases remain undiagnosed as a result of the impracticality of neuropsychological testing, particularly in primary care. Conclusion: The large number of available batteries can be beneficial to the clinician or researcher however, care should be taken in order to choose the correct battery for each application.Įarly detection and diagnosis are critical to dementia care. Discriminant validity and test–retest reliability were well documented for most batteries while documentation of other psychometric properties varied. All batteries exhibit strengths associated with computerized testing such as standardization of administration, accurate measurement of many variables, automated record keeping, and savings of time and costs. Computerized adaptive testing (CAT) and the Cambridge Cognitive Examination CAT battery as well as 3 experimental batteries and an experimental test are discussed in separate sections. Results: Seventeen test batteries were identified and categorized according to their scope.
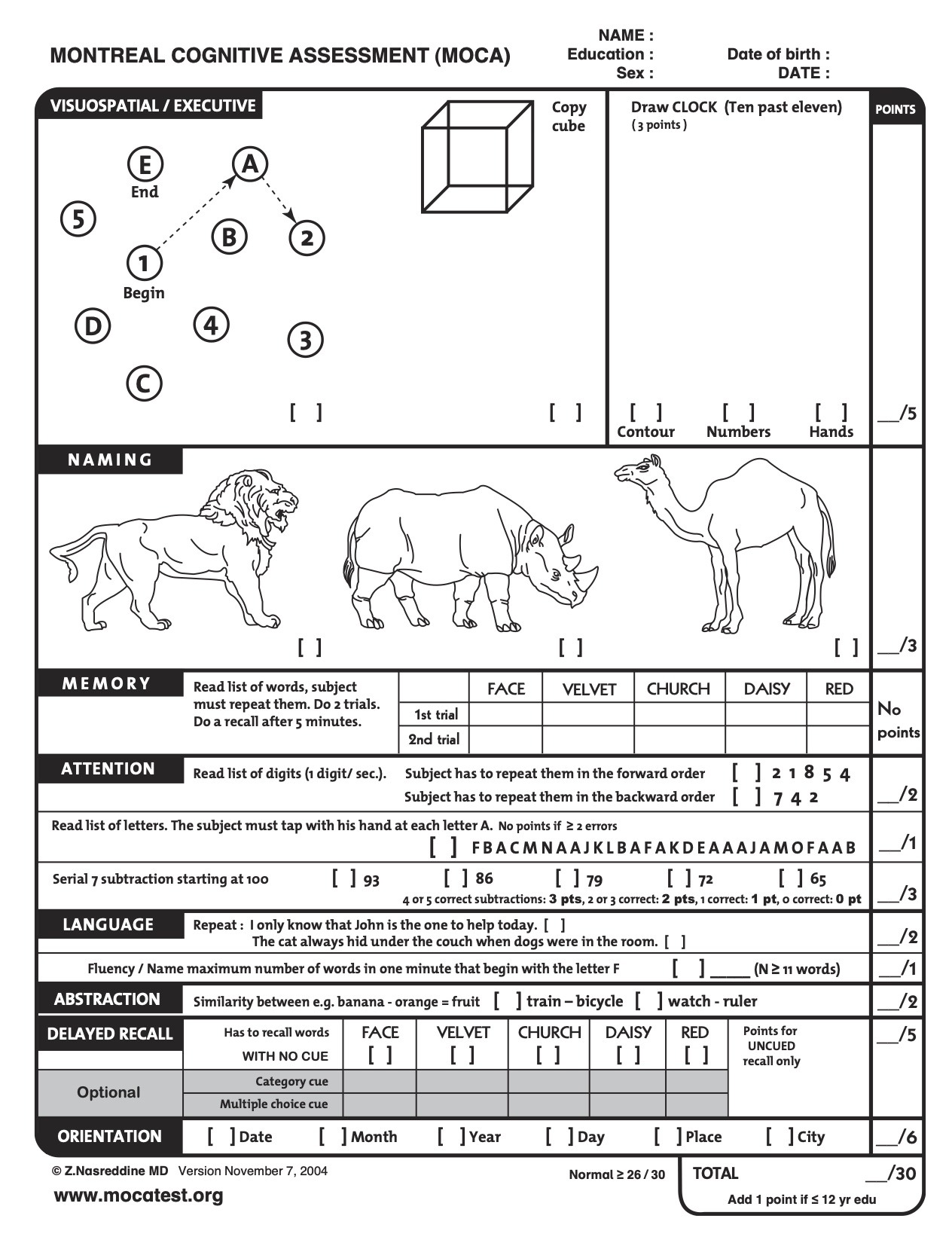

Method: A literature search on Medline followed by cross-referencing yielded a total of 76 citations. Objective: This article is a review of computerized tests and batteries used in the cognitive assessment of older adults.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
